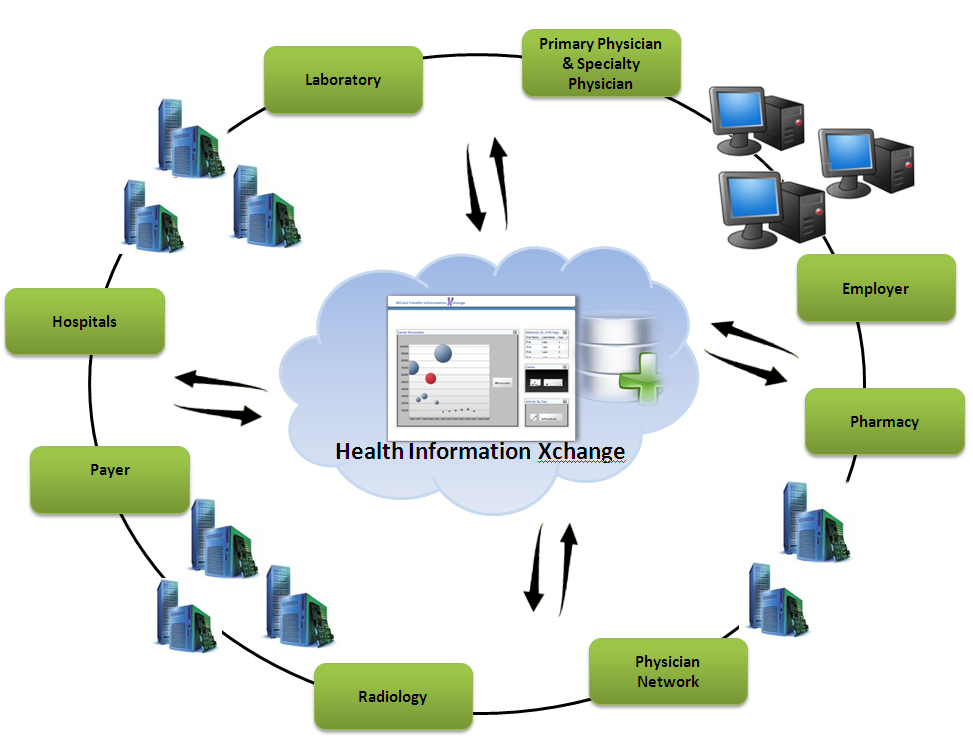
Health information systems (HIS) have become an integral part of modern healthcare, revolutionizing the way medical data is managed and utilized. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the importance of efficient and accurate information management cannot be overstated. HIS plays a pivotal role in streamlining clinical processes, ensuring patient safety, and improving overall healthcare delivery. In this article, we will explore what health information systems are, their components, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
The adoption of health information systems has transformed the healthcare landscape by providing a digital infrastructure for storing, managing, and sharing patient data. These systems have enabled healthcare providers to make informed decisions, reduce medical errors, and enhance patient outcomes. With the increasing demand for interoperability and data-driven insights, HIS continues to evolve, offering innovative solutions to address the complexities of modern healthcare.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of health information systems, focusing on their significance, functionalities, and impact on the healthcare industry. Whether you are a healthcare professional, IT specialist, or simply interested in understanding the role of technology in healthcare, this article will serve as a valuable resource.
Read also:Advantages Of Being In The Army Unlocking The Path To Growth And Success
Table of Contents
- What Are Health Information Systems?
- A Brief History of Health Information Systems
- Key Components of Health Information Systems
- Types of Health Information Systems
- Benefits of Health Information Systems
- Challenges in Implementing Health Information Systems
- Data Security and Privacy in Health Information Systems
- Integration with Other Healthcare Technologies
- Future Trends in Health Information Systems
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What Are Health Information Systems?
Health information systems (HIS) refer to a collection of software, hardware, and processes designed to manage and analyze healthcare data. These systems are used to store, retrieve, and share patient information, clinical records, and administrative data. The primary goal of HIS is to improve the quality of healthcare delivery by providing healthcare professionals with accurate and timely information.
At its core, a health information system acts as a central repository for all medical data, enabling seamless communication between healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders. By integrating various components such as electronic health records (EHR), laboratory information systems (LIS), and radiology information systems (RIS), HIS ensures that all relevant information is accessible when needed.
Why Are Health Information Systems Important?
Health information systems are crucial for modern healthcare due to their ability to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes. They enable healthcare providers to make data-driven decisions, streamline clinical workflows, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Furthermore, HIS facilitates collaboration among healthcare professionals, leading to better-coordinated care for patients.
A Brief History of Health Information Systems
The concept of health information systems dates back to the early 20th century when hospitals began using manual record-keeping methods to manage patient data. However, the advent of computers in the mid-20th century marked a turning point in the evolution of HIS. The first electronic medical record systems were introduced in the 1960s, laying the foundation for modern health information systems.
Over the years, HIS has undergone significant advancements, driven by technological innovations and increasing demand for digital solutions in healthcare. Today, health information systems are sophisticated platforms that integrate multiple functionalities, offering unparalleled capabilities for data management and analysis.
Key Milestones in the Development of HIS
- 1960s: Introduction of the first electronic medical record systems.
- 1980s: Emergence of computerized physician order entry (CPOE) systems.
- 1990s: Development of interoperability standards, such as HL7.
- 2000s: Widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHR) and health information exchanges (HIE).
Key Components of Health Information Systems
A health information system consists of several interconnected components that work together to ensure efficient data management and analysis. These components include hardware, software, databases, and communication networks. Below are the key components of a typical HIS:
Read also:Rob Kardashian Sr The Untold Story Of The Kardashian Family Patriarch
1. Electronic Health Records (EHR)
EHRs are digital versions of patient medical records that contain comprehensive information about a patient's health history, diagnosis, treatment plans, and medications. EHRs are a critical component of HIS, enabling healthcare providers to access patient data quickly and securely.
2. Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
Laboratory information systems are used to manage and analyze data generated by clinical laboratories. LIS automates the process of specimen tracking, test result reporting, and quality control, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in laboratory operations.
3. Radiology Information Systems (RIS)
Radiology information systems are designed to manage radiology workflows, including patient scheduling, image acquisition, and result reporting. RIS integrates with picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) to store and retrieve medical images, enabling radiologists to access diagnostic information easily.
Types of Health Information Systems
Health information systems come in various forms, each tailored to meet specific needs within the healthcare industry. Below are some common types of HIS:
1. Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
Hospital information systems are comprehensive platforms that integrate all aspects of hospital operations, including patient care, administrative tasks, and financial management. HIS ensures seamless communication between different departments, improving overall hospital efficiency.
2. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical decision support systems are designed to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions by providing real-time clinical guidelines, alerts, and recommendations based on patient data. CDSS enhances diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning, leading to better patient outcomes.
3. Telemedicine Systems
Telemedicine systems enable remote healthcare delivery through the use of communication technologies. These systems allow patients to consult with healthcare providers from a distance, improving access to care, especially in underserved areas.
Benefits of Health Information Systems
Health information systems offer numerous benefits to healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders. Below are some of the key advantages of implementing HIS:
1. Improved Patient Care
HIS enables healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient data, leading to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. This results in improved patient outcomes and higher satisfaction levels.
2. Enhanced Efficiency
By automating routine tasks and streamlining workflows, HIS reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers, allowing them to focus more on patient care. This leads to increased productivity and cost savings.
3. Better Data Management
HIS provides a centralized platform for storing and managing healthcare data, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. This facilitates data-driven decision-making and supports research and innovation in healthcare.
Challenges in Implementing Health Information Systems
Despite their numerous benefits, implementing health information systems comes with its own set of challenges. Below are some common obstacles faced during HIS implementation:
1. High Initial Costs
The cost of purchasing, installing, and maintaining health information systems can be significant, especially for smaller healthcare facilities. This financial burden may deter some organizations from adopting HIS.
2. Resistance to Change
Healthcare professionals may resist adopting new technologies due to concerns about workflow disruptions and the need for additional training. Overcoming this resistance requires effective change management strategies and stakeholder engagement.
3. Interoperability Issues
Ensuring seamless integration between different health information systems and external platforms remains a challenge. Standardization and adherence to interoperability guidelines are essential to address this issue.
Data Security and Privacy in Health Information Systems
Data security and privacy are critical considerations in the design and implementation of health information systems. With the increasing amount of sensitive patient data being stored and shared digitally, ensuring the protection of this information is paramount. Below are some best practices for securing health information systems:
1. Encryption
Encrypting data during transmission and storage helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. HIS should incorporate robust encryption protocols to safeguard patient data.
2. Access Controls
Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized personnel can access patient information. Role-based access management and multi-factor authentication are effective strategies for enhancing data security.
Integration with Other Healthcare Technologies
Health information systems are increasingly being integrated with other healthcare technologies to create a cohesive digital ecosystem. This integration enables seamless data exchange and collaboration among various stakeholders in the healthcare industry. Below are some examples of HIS integration:
1. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The integration of HIS with IoMT devices allows for real-time monitoring of patient health metrics, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML technologies are being used to analyze large volumes of healthcare data, providing valuable insights for clinical decision-making and predictive analytics.
Future Trends in Health Information Systems
The future of health information systems is shaped by emerging technologies and evolving healthcare needs. Below are some trends that are likely to influence the development of HIS in the coming years:
1. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud computing offers scalable and cost-effective solutions for storing and managing healthcare data. HIS providers are increasingly adopting cloud-based platforms to enhance flexibility and accessibility.
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize data security and interoperability in health information systems. Its decentralized and immutable nature ensures the integrity and traceability of healthcare data.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, health information systems play a vital role in modern healthcare by providing a digital infrastructure for managing and analyzing medical data. From improving patient care to enhancing operational efficiency, HIS offers numerous benefits that make it an indispensable tool for healthcare providers. However, successful implementation requires addressing challenges such as high costs, resistance to change, and interoperability issues.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with health information systems in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore our other articles on healthcare technology and innovation. Together, let's shape the future of healthcare!
References:
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2021). Digital Health. Retrieved from https://www.who.int
- HealthIT.gov. (2022). Health Information Technology. Retrieved from https://www.healthit.gov
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2020). Electronic Health Records. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov