Military ranks and pay grades are crucial components of the armed forces that define a service member's responsibilities, authority, and compensation. Whether you're a prospective enlistee, a veteran, or simply interested in understanding how military structures work, this article will provide you with detailed insights. From the hierarchy of ranks to the pay scales associated with each grade, we will break down everything you need to know.
The military is a highly organized institution, and understanding its rank structure and pay grades is essential for anyone considering a career in the armed forces. This guide aims to shed light on how ranks are structured, the responsibilities tied to each rank, and how compensation is determined based on these ranks.
By exploring the intricacies of military ranks and pay grades, we hope to provide clarity and help individuals make informed decisions about their military careers. Let's dive into the world of military hierarchy and compensation.
Read also:Karlan Denio Connie Denio The Ultimate Guide To Their Journey And Impact
Table of Contents
- Overview of Military Ranks and Pay Grades
- Understanding Military Rank Structure
- What Are Military Pay Grades?
- Enlisted Ranks and Responsibilities
- Officer Ranks and Leadership Roles
- Warrant Officers: Bridging the Gap
- Military Pay Scales and Compensation
- Additional Benefits Beyond Pay
- Promotion Process and Criteria
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Overview of Military Ranks and Pay Grades
Military ranks and pay grades form the backbone of the armed forces, providing a clear hierarchy and structure for effective command and control. Each rank carries specific responsibilities and expectations, ensuring the smooth operation of military units. Understanding the relationship between ranks and pay grades is vital for service members and those considering a military career.
The rank structure in the military is designed to establish authority and accountability at every level. Pay grades, on the other hand, determine the financial compensation a service member receives based on their rank and years of service. This dual system ensures that individuals are rewarded for their dedication and experience.
In this section, we will explore the foundational aspects of military ranks and pay grades, setting the stage for a deeper dive into each component.
Understanding Military Rank Structure
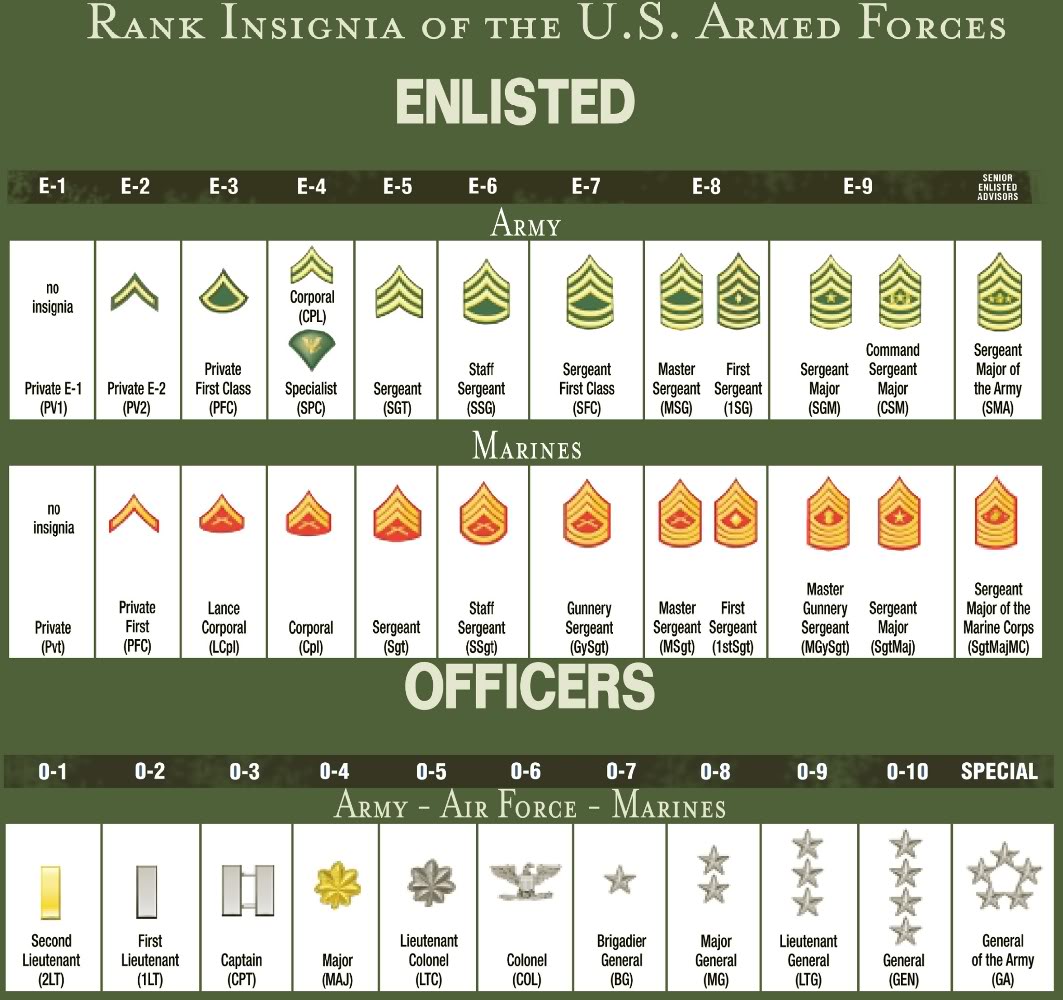
The military rank structure is divided into three main categories: enlisted personnel, warrant officers, and commissioned officers. Each category has its own set of ranks and responsibilities, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the armed forces.
Categories of Military Ranks
- Enlisted Personnel: These are the backbone of the military, responsible for carrying out orders and performing essential duties.
- Warrant Officers: They serve as technical experts and provide specialized knowledge and skills.
- Commissioned Officers: These individuals hold leadership positions and are responsible for strategic decision-making.
Each category plays a critical role in the military hierarchy, ensuring that tasks are executed efficiently and effectively.
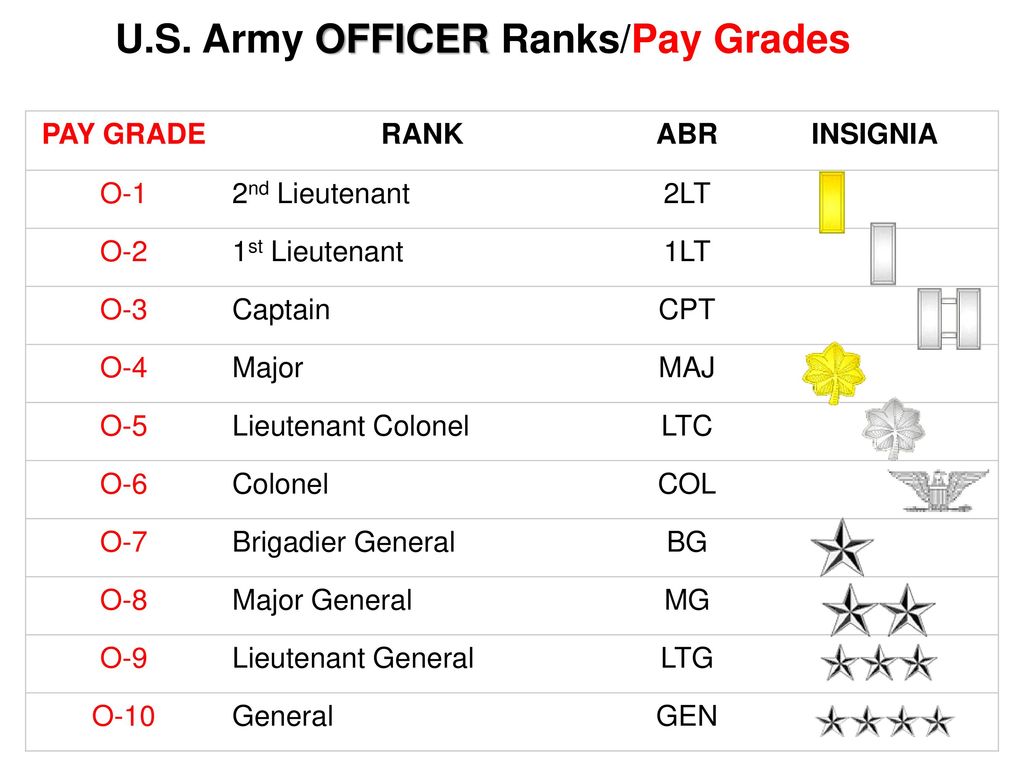
What Are Military Pay Grades?
Military pay grades are designations assigned to each rank, determining the level of compensation a service member receives. These grades range from E-1 for the lowest enlisted rank to O-10 for the highest commissioned officer rank. Pay grades are crucial in establishing a fair and standardized system of compensation across all branches of the military.
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Choctaw Health Clinic Your Trusted Healthcare Provider
Pay grades are directly linked to the responsibilities and experience associated with each rank. For example, an E-1 private will earn significantly less than an O-6 colonel due to the difference in rank and years of service.
This section will delve deeper into the specifics of pay grades and how they are calculated.
Enlisted Ranks and Responsibilities
Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the military, performing a wide range of duties essential to the operation of the armed forces. These individuals start at the lowest ranks and work their way up through promotions based on performance and experience.
Key Enlisted Ranks
- Private (E-1): The entry-level rank for enlisted personnel, responsible for basic duties.
- Corporal (E-4): Supervises small teams and assists higher-ranking personnel.
- Sergeant Major (E-9): The highest enlisted rank, advising senior officers on enlisted matters.
Enlisted ranks are crucial for executing day-to-day operations and ensuring the military's mission is accomplished.
Officer Ranks and Leadership Roles
Commissioned officers hold leadership positions and are responsible for strategic planning and decision-making. These individuals undergo extensive training and education to prepare them for their roles in commanding military units.
Key Officer Ranks
- Second Lieutenant (O-1): The entry-level rank for commissioned officers, typically leading platoons.
- Major (O-4): Commands battalions and provides leadership at the company level.
- General (O-10): The highest rank, responsible for overseeing entire branches of the military.
Officer ranks are integral to the command structure, ensuring that operations are planned and executed with precision.
Warrant Officers: Bridging the Gap
Warrant officers occupy a unique position in the military hierarchy, bridging the gap between enlisted personnel and commissioned officers. They are technical experts in specific fields, providing specialized knowledge and skills to their units.
Warrant officers often serve as advisors and trainers, ensuring that their expertise is utilized effectively. This section will explore the role of warrant officers and their contributions to the military.
Military Pay Scales and Compensation
Military pay scales are designed to provide fair and equitable compensation based on rank and years of service. These scales are updated regularly to reflect changes in the cost of living and economic conditions.
Factors Affecting Pay
- Rank: Higher ranks generally receive higher pay.
- Years of Service: Longer service often results in increased compensation.
- Location: Service members stationed in high-cost areas may receive additional allowances.
This section will provide a detailed breakdown of military pay scales and how they are calculated.
Additional Benefits Beyond Pay
In addition to base pay, service members receive a variety of benefits that enhance their overall compensation package. These benefits include healthcare, retirement plans, and housing allowances.
Understanding the full scope of military benefits is essential for service members and their families, as these perks contribute significantly to their quality of life.
Promotion Process and Criteria
Promotion within the military is a competitive process that requires individuals to meet specific criteria and demonstrate exceptional performance. Factors such as leadership potential, technical skills, and years of service are all considered during the promotion process.
This section will outline the steps involved in the promotion process and the importance of meeting the necessary requirements.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Military ranks and pay grades are fundamental to the structure and function of the armed forces. By understanding the hierarchy and compensation associated with each rank, service members can make informed decisions about their careers and future opportunities.
We encourage readers to explore further resources and consider the benefits of a military career. If you found this article helpful, please share it with others and leave a comment below with your thoughts and questions. For more information on military topics, check out our other articles on the site.
Data Sources: U.S. Department of Defense, Military Benefits, and Federal Pay Tables.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/united-states-military-ranks-and-pay-grades-3357045-FINAL-5be9a98646e0fb0051db4600-6fc56a6f954c4ba6baf88c66901df974.png)