Naval ranks form the backbone of any maritime force, organizing personnel into structured hierarchies that ensure operational efficiency and discipline. Whether you're a military enthusiast or someone interested in understanding the naval hierarchy, this article will guide you through the ranks in detail. From the lowest to the highest, we will explore the roles and responsibilities that define each rank.
Throughout history, naval ranks have evolved to meet the demands of modern warfare and maritime exploration. These ranks not only signify authority but also represent the skills and expertise required to lead and serve in one of the world's most disciplined forces.
This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of naval ranks, breaking them down into easily digestible sections while maintaining the integrity of the information. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the naval hierarchy and its significance.
Read also:Star Sign Birthdays Unlock The Secrets Of Your Zodiac Personality
Table of Contents
- Biography of Naval Ranks
- History of Naval Ranks
- Lowest Naval Ranks
- Mid-Level Naval Ranks
- Senior Naval Ranks
- Flag Officers and Their Roles
- Specialized Naval Ranks
- Naval Rank Structure and Hierarchy
- International Differences in Naval Ranks
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Biography of Naval Ranks
Naval ranks have a storied history that dates back centuries. To fully appreciate their significance, it's important to understand their origins and evolution. Below is a brief overview of key aspects:
Data and Biodata of Naval Ranks
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin | Medieval naval traditions |
| Purpose | To establish order and command |
| Evolution | Adapted to modern military needs |
| Current Usage | Used globally in naval forces |
History of Naval Ranks
The history of naval ranks is as old as maritime exploration itself. From ancient times to the modern era, the structure of naval ranks has undergone significant changes. Initially, ranks were informal and based on experience and leadership qualities. Over time, they became formalized, reflecting the growing complexity of naval operations.
During the Age of Exploration, naval ranks began to take shape as nations expanded their territories. The British Royal Navy, in particular, played a pivotal role in shaping the modern naval hierarchy. By the 18th century, a structured system of ranks was established, which has influenced naval forces worldwide.
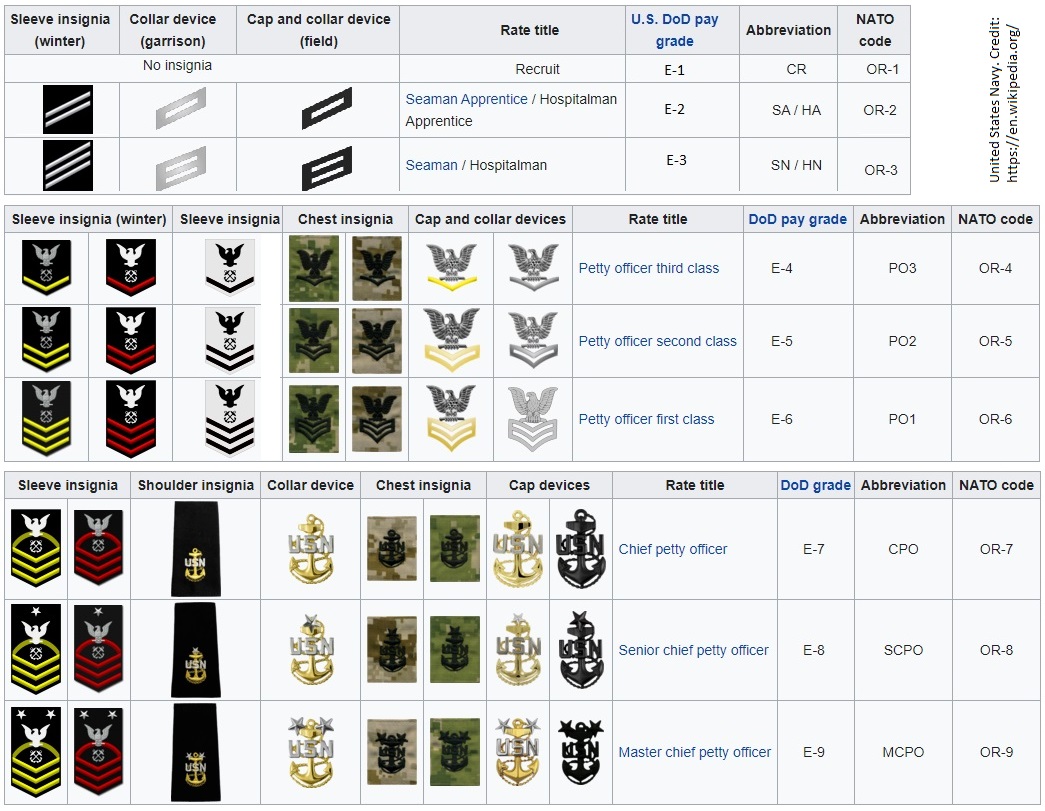
Lowest Naval Ranks
At the foundation of the naval hierarchy are the lowest ranks. These positions are typically held by individuals who are new to the service and are still learning the ropes. Below are some of the lowest naval ranks:
Seaman and Ratings
- Seaman Recruit: The lowest rank in the navy, usually held by new recruits.
- Seaman Apprentice: A step above recruit, indicating basic training completion.
- Seaman: The next rank, where individuals gain more responsibility.
These ranks emphasize discipline and teamwork, preparing sailors for more advanced roles within the navy.
Mid-Level Naval Ranks
Mid-level ranks represent a transition from basic duties to leadership roles. Individuals at this level are expected to demonstrate leadership qualities and technical expertise. Some key mid-level ranks include:
Read also:Unveiling The Legacy Of Jason Mrax A Comprehensive Guide
Non-Commissioned Officers
- Petty Officer Third Class: The first rank in the NCO category.
- Petty Officer Second Class: A step higher, with increased responsibility.
- Petty Officer First Class: The highest NCO rank before senior leadership.
Mid-level ranks focus on mentoring junior sailors and executing orders from higher-ranking officers.
Senior Naval Ranks
Senior ranks signify a higher level of authority and responsibility. These positions require extensive experience and leadership skills. Key senior ranks include:
Chief Petty Officers
- Chief Petty Officer: The first rank in the senior NCO category.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer: A higher rank with greater influence.
- Master Chief Petty Officer: The highest enlisted rank, often serving as advisors to senior officers.
Senior ranks play a crucial role in bridging the gap between enlisted personnel and commissioned officers.
Flag Officers and Their Roles
Flag officers represent the pinnacle of naval hierarchy. These ranks include admirals and other high-ranking officials who oversee large-scale operations. Key flag officer ranks include:
Admiral Ranks
- Rear Admiral: The first flag officer rank, commanding smaller fleets.
- Vice Admiral: A higher rank, responsible for larger operations.
- Admiral: The highest rank in most navies, overseeing entire fleets.
Flag officers are responsible for strategic planning and decision-making at the highest levels.
Specialized Naval Ranks
In addition to traditional ranks, some navies have specialized ranks for specific roles. These ranks cater to unique skill sets and responsibilities. Examples include:
Specialized Roles
- Naval Aviator: Pilots trained for maritime operations.
- Seal Team Member: Elite commandos specializing in covert operations.
- Marine Corps Officer: Officers trained for amphibious operations.
Specialized ranks highlight the diversity of roles within the naval forces.
Naval Rank Structure and Hierarchy
The structure of naval ranks is designed to ensure clear lines of authority and communication. From the lowest to the highest, each rank has a defined role and responsibility. The hierarchy is divided into enlisted personnel, non-commissioned officers, and commissioned officers, with flag officers at the top.
This structured approach facilitates effective command and control, enabling navies to operate efficiently in complex environments.
International Differences in Naval Ranks
While the basic structure of naval ranks is similar across nations, there are some differences. These variations reflect cultural, historical, and operational factors unique to each country. For example:
Comparative Analysis
- United States Navy: Uses a detailed rank system with specific titles.
- Royal Navy (UK): Incorporates traditional titles with modern roles.
- Indian Navy: Combines British traditions with local customs.
Understanding these differences provides insight into the global diversity of naval forces.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, naval ranks from lowest to highest form a structured hierarchy that ensures the smooth functioning of naval operations. By understanding the roles and responsibilities associated with each rank, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and discipline of naval forces.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from it. For further reading, explore our other articles on military history and strategies.
Data sourced from reputable military publications and historical records, including the U.S. Navy official website and the Royal Navy's historical archives.