In today's rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, a health information system (HIS) plays an indispensable role in managing and optimizing healthcare delivery. HIS has become the backbone of modern healthcare facilities, enabling seamless communication, data sharing, and efficient decision-making. Understanding what a health information system is and its significance is crucial for healthcare providers, administrators, and patients alike.
As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, the adoption of HIS has become a necessity rather than a luxury. This system not only streamlines administrative tasks but also enhances patient care by providing real-time access to critical health information. From managing electronic health records (EHRs) to facilitating telemedicine services, HIS is transforming the way healthcare is delivered.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the concept of a health information system, its components, benefits, challenges, and future prospects. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a technology enthusiast, or simply curious about the intersection of healthcare and technology, this article will provide you with valuable insights and actionable knowledge.
Read also:Unveiling The F5e Jet A Comprehensive Guide To One Of The Worlds Most Iconic Fighter Aircraft
Table of Contents
- What is a Health Information System?
- The History and Evolution of Health Information Systems
- Key Components of a Health Information System
- Benefits of Implementing a Health Information System
- Challenges in Adopting a Health Information System
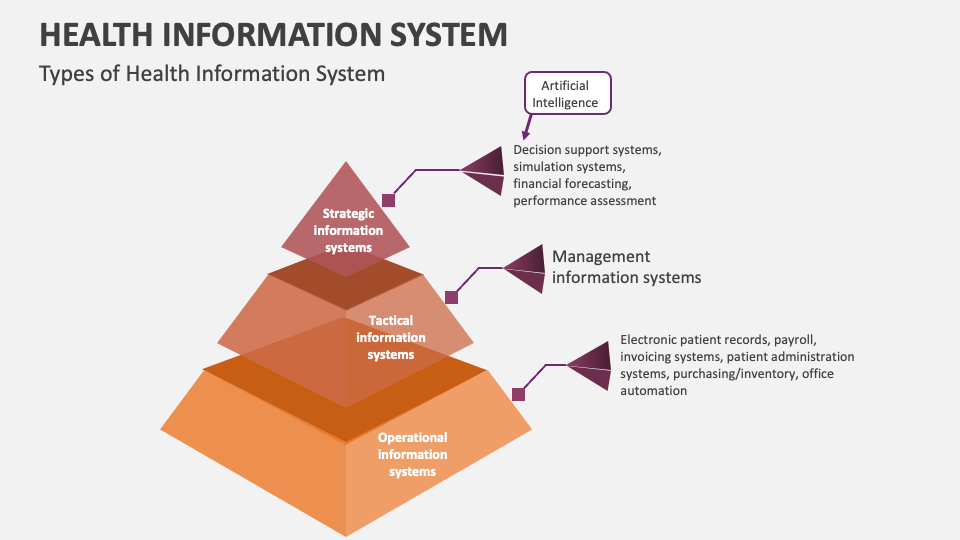
- Types of Health Information Systems
- Data Management in Health Information Systems
- Ensuring Data Security and Privacy in HIS
- The Future of Health Information Systems
- Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Health Information Systems
What is a Health Information System?
A health information system (HIS) refers to a digital infrastructure designed to collect, store, manage, and transmit health-related data. It serves as a centralized platform that facilitates the exchange of information between healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders. HIS is not just a software application but a comprehensive framework that integrates various tools and technologies to enhance healthcare delivery.
The primary goal of a health information system is to improve the quality of care by ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to accurate and up-to-date patient information. This system enables the automation of administrative tasks, reduces errors, and promotes efficient resource utilization. By leveraging HIS, healthcare organizations can achieve better outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Why is a Health Information System Important?
The importance of a health information system cannot be overstated in today's data-driven healthcare environment. HIS provides several advantages, including:
- Enhanced patient safety through accurate and accessible medical records.
- Improved communication and collaboration among healthcare providers.
- Streamlined administrative processes, reducing the burden on staff.
- Facilitation of evidence-based decision-making through data analytics.
The History and Evolution of Health Information Systems
The concept of health information systems dates back to the mid-20th century when healthcare providers began exploring ways to digitize patient records. Initially, these systems were rudimentary and focused primarily on administrative tasks such as billing and scheduling. However, with advancements in technology, HIS has evolved into a sophisticated platform that integrates clinical, financial, and operational data.
Over the years, the development of electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and health information exchanges (HIEs) has further expanded the capabilities of HIS. Today, these systems are capable of handling complex data sets, supporting artificial intelligence applications, and enabling remote patient monitoring.
Key Components of a Health Information System
A health information system comprises several essential components that work together to ensure its functionality and effectiveness. These components include:
Read also:Understanding Dependent Pay Military A Comprehensive Guide
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs are digital versions of a patient's medical history, which include information such as diagnoses, treatments, medications, and test results. They provide healthcare providers with a comprehensive view of a patient's health status, enabling them to make informed decisions.
2. Practice Management Software
This component focuses on automating administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and insurance claims processing. It helps healthcare organizations improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
3. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
CDSS provides healthcare professionals with evidence-based recommendations and alerts to assist in decision-making. These systems analyze patient data and offer suggestions for diagnosis, treatment, and medication management.
Benefits of Implementing a Health Information System
The implementation of a health information system offers numerous benefits for healthcare organizations, providers, and patients. Some of these benefits include:
- Improved Patient Care: HIS enables healthcare providers to access real-time patient data, leading to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of administrative tasks reduces the workload on staff, allowing them to focus on patient care.
- Cost Savings: By minimizing errors and optimizing resource utilization, HIS helps healthcare organizations reduce costs.
- Increased Transparency: HIS promotes transparency in healthcare delivery by providing patients with access to their medical records and treatment plans.
Challenges in Adopting a Health Information System
Despite its numerous advantages, the adoption of a health information system is not without challenges. Some of the common challenges include:
1. High Implementation Costs
Implementing a comprehensive HIS requires significant investment in hardware, software, and training. This can be a barrier for small and medium-sized healthcare organizations.
2. Resistance to Change
Healthcare providers and staff may resist adopting new technologies due to fear of the unknown or concerns about the learning curve. Effective change management strategies are essential to overcome this challenge.
3. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
With the increasing amount of sensitive patient data being stored and transmitted, ensuring data security and privacy is a top priority. Healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures to protect against data breaches and cyberattacks.
Types of Health Information Systems
There are several types of health information systems, each designed to address specific needs and requirements. These include:
1. Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
Hospital information systems are designed to manage all aspects of hospital operations, from patient care to financial management. They provide a comprehensive platform for integrating clinical, administrative, and financial data.
2. Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
Laboratory information systems focus on managing laboratory operations, including specimen tracking, test result management, and quality control. They ensure the accuracy and reliability of laboratory data.
3. Radiology Information Systems (RIS)
Radiology information systems are used to manage radiology workflows, including scheduling, reporting, and image archiving. They enhance the efficiency and accuracy of radiology services.
Data Management in Health Information Systems
Effective data management is crucial for the success of a health information system. HIS must ensure that data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. This involves implementing standardized data entry protocols, regular data audits, and data governance policies.
Data management in HIS also involves the use of advanced analytics tools to derive insights from large data sets. These insights can be used to improve patient care, optimize resource allocation, and enhance operational efficiency.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy in HIS
Data security and privacy are paramount in health information systems. Healthcare organizations must adhere to regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to protect patient data. This involves implementing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Additionally, healthcare organizations should educate staff on data security best practices and conduct regular training sessions to ensure compliance with security protocols. By prioritizing data security, organizations can build trust with patients and stakeholders.
The Future of Health Information Systems
The future of health information systems looks promising, with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) set to transform the healthcare landscape. These technologies will enable HIS to become more intelligent, secure, and interconnected.
AI-powered HIS will be capable of predicting patient outcomes, identifying potential health risks, and personalizing treatment plans. Blockchain technology will enhance data security and interoperability, while IoT devices will facilitate real-time monitoring and remote patient care.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Health Information Systems
In conclusion, a health information system is a vital tool for modern healthcare organizations, enabling them to deliver high-quality care while optimizing operational efficiency. By understanding the components, benefits, and challenges of HIS, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its implementation and adoption.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with health information systems in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into healthcare technology and innovation. Together, let's embrace the power of health information systems to transform healthcare for the better!
References:
- World Health Organization. (2020). Health Information Systems. Retrieved from https://www.who.int.
- HealthIT.gov. (2021). Electronic Health Records. Retrieved from https://www.healthit.gov.